Soup 51, December 23, 2022
| Soup | 51 |
|---|---|
| Permalink | Permalink |
| Date | 2022-12-23 |
| Twitter/X | Read |
| Twitter/X Quotes | View |
| Twitter/X Latest Comments | View |
| Twitter/X Thread | Thread |
| Thread Reader App | Read |
| Thread Reader PDF | Read |
| Profession | Information |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | The russia |
| Retweets | 228 |
| Likes | 651 |
| Views | 131.8k |
| Bookmarks | 89 |
| Topics | |
| In other languages | Russkiy mir 2 (es) Russkiy mir 2 (it) |
| Related soups: |
Russkiy mir 2
Narodnost is Russia’s version of nationality. The definition of Narodnost came from Russia’s leadership, rather than the population itself. The idea behind Narodnost is that Russian people should be ready to sacrifice themselves for the Tsar, for the country.
The fall of USSR also led to two realities: the one in the public sphere and the one at home. In the public sphere, everything was fine and dandy, but at home people were criticizing the whole system.
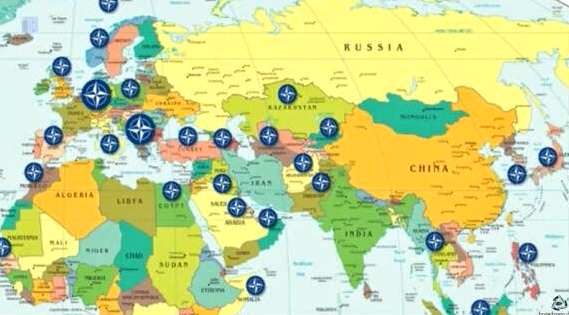
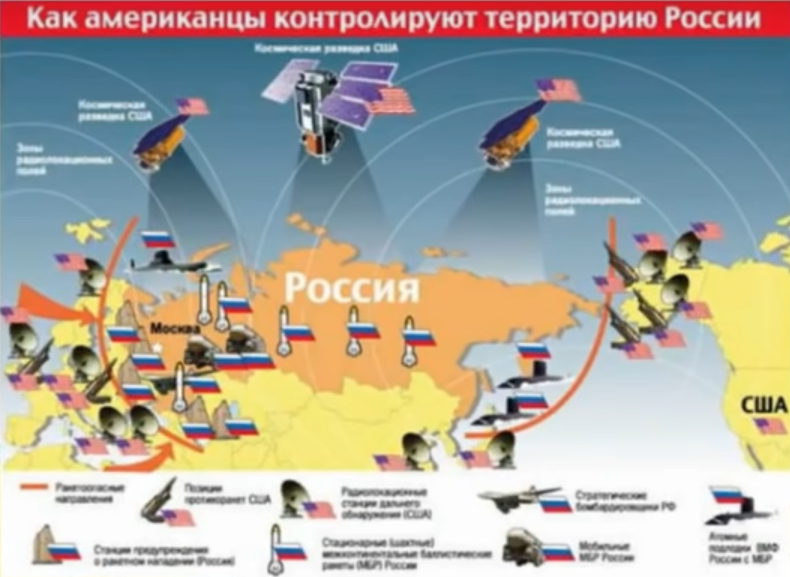
So the Russians are used to being the target of invasions, which of course affects their worldview.
Whereas US imperialism is based on gathering resources such as oil and precious metals, …
Whereas US imperialism is based on gathering resources such as oil and precious metals, …
… Russian imperialism is built on fear — the idea that enemy is constantly at the gates is used to reinforce the idea of invasions, buffer states, etc. It’s what one could call “defensive imperialism”.
To conclude, Nicholas I stated during the 19th century that “constant small-scale war at Russia’s borders is necessary to keep the patriotism alive.” This kind of thinking is still very strong inside the Russian leadership.
Source:
Source:
 Russkiy mir
Russkiy mir